On the Computational Design of Azobenzene-Based Multi-State Photoswitches
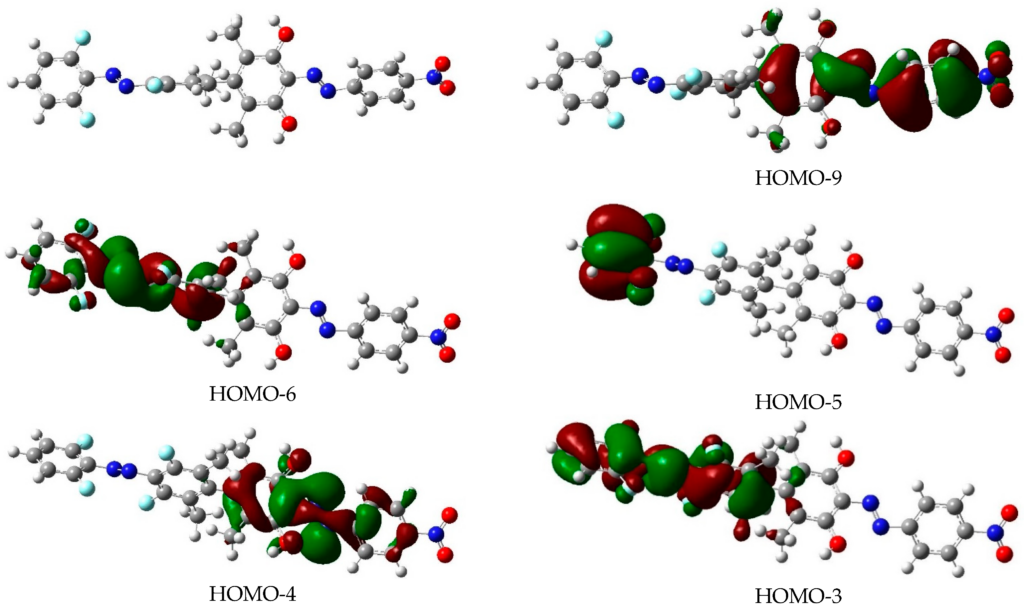
In order to theoretically design multi-state photoswitches with specific properties, an exhaustive computational study is first carried out for an azobenzene dimer that has been recently synthesized and experimentally studied. This study allows for a full comprehension of the factors that govern the photoactivated isomerization processes of these molecules so to provide a conceptual/computational protocol that can be applied to generic multi-state photoswitches. From this knowledge a new dimer with a similar chemical design is designed and also fully characterized. Our theoretical calculations predict that the new dimer proposed is one step further in the quest for a double photoswitch, where the four metastable isomers could be selectively interconverted through the use of different irradiation sequences.